So What is Reinforcement Learning
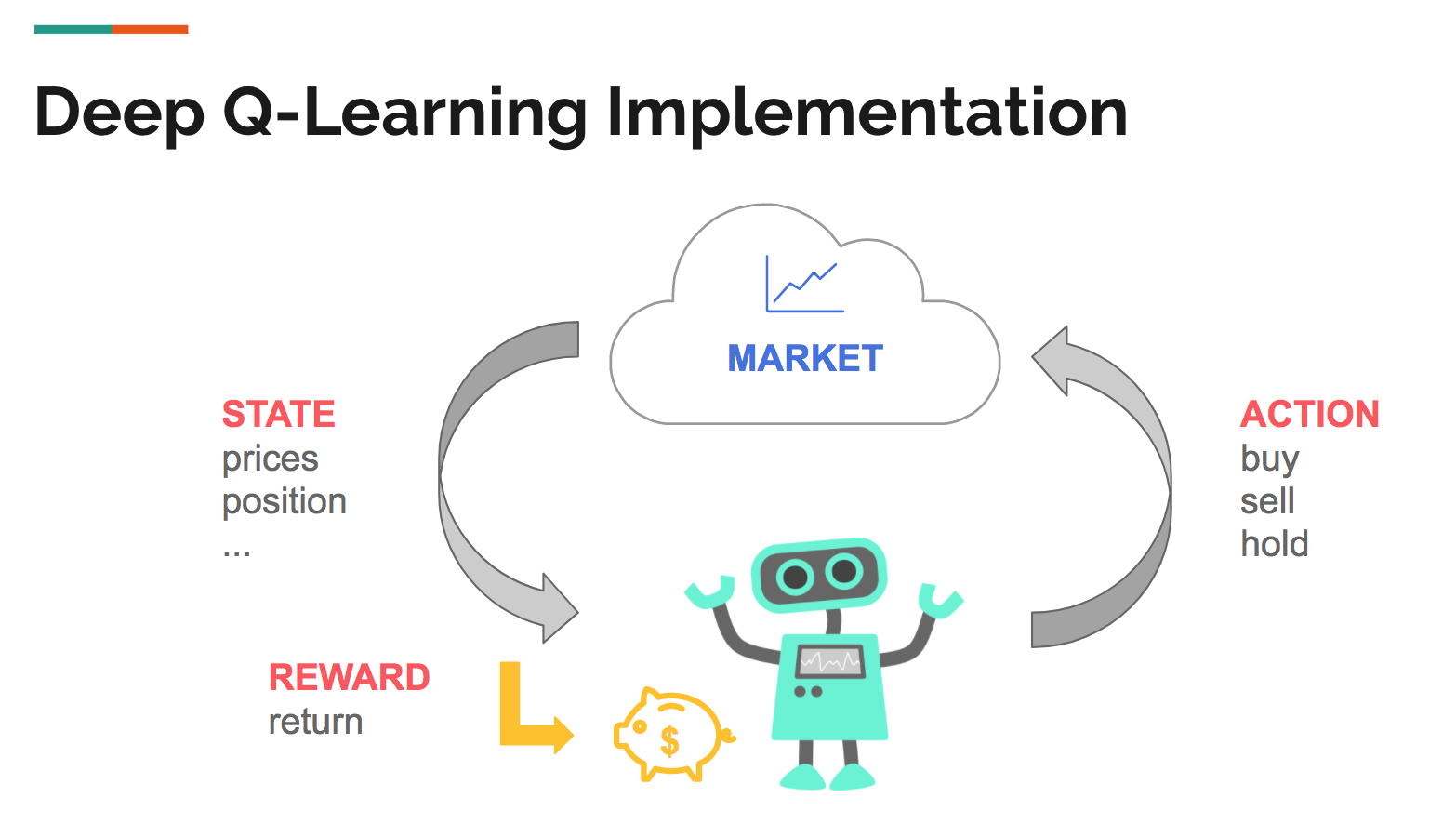
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a type of machine learning that allows the agent to learn from its environment based on a reward feedback system. One of the most well known examples of RI is AlphaGo, developed by Alphabet Inc.’s Google Deepmind. It was trained using a number of machine learning models, including RI, to learn how to play the notoriously challenging board game Go and went on to beat the world’s greatest players. This feat was thought of as impossible with the technology available at the time.
The main difference between RL and traditional machine learning is that reinforcement learning tries to solve a reward maximization problem over multiple steps (aka stochastic sequential decision processes). Instead of supervised learning with a clear feedback, reinforcement learning is about scores and rewards.
So how does RI actually work? One example allows the software agent to select an action that will maximise the reward in the long term. We don’t tell the software what to do, but instead it learns from its own environment and experience. This is one of the differences between reinforcement learning and supervised learning.